This program is a very simple one, it is designed to showcase how to read a file into SIMPOL as well as output to a file using SIMPOL. This is part of a series of tutorials which builds up to a program which will read a file, manipulate its contents and then formats the information into a more useful format (that can be found here)
Input
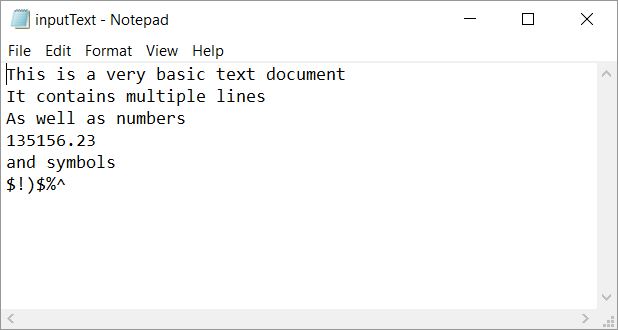
After we’ve created our project we will then need to create a file which will be read into the program, this needs to be put in the bin folder within our project. A sample text document has been provided in the project zip file, but you should try and create one yourself, it should ideally contain multiple lines as well as symbol and numbers, this should allow you to cover the basics of file I/O within superbase.
This text file should be named something sensible as we are going to need to use it to access the file. At this point we can go to the IDE and write our first bit of code:
function main()
fsfileinputstream input
string sInputfile
integer errornoThese variables correspond to the file input object, a string for the input filename, and an integer for error checking.
To open our file we are going to need to declare our input object like so:
file =@ fsfileinputstream.new(sInputfile, errorno)For this code to run correctly, we need to initialise both of these variables, inputfile needs to contain the filename (including the file extension) and although errorno does not need to be declared it is clever to set it to a number which does not correlate to an error code (such as -1). Thus the full code should look like this
sInputfile = "inputText.txt"
errorno = -1
input =@ fsfileinputstream.new(sInputfile, errorno)Something that was not previously mentioned is the use of the =@ to declare the input object, this symbol signifies that the right side of the assignment operator (equals sign) is assigned to the left side of the operator. This program should now execute without error, although it is not very useful yet that comes now
Getting Data
We have now opened our file into SIMPOL, we now want to get a text from the file so we can use it. There are three ways of getting data (as well as corresponding functions for writing) these vary in what type they return: blob, integer, or string. In our case, we will be primarily using getstring() but getblob() and getinteger()can be equally useful. getblob() returns a blob containing bytes from the folder and you can specify the number of bytes to return. getinteger() does very much the same thing, attempts to return integers read from the file, here you can choose how many integers to read and whether these are signed or unsigned integers. getstring() is a comparatively complex function, with five variables: length, charsize, lbo, terminator, terminatedby. These respectively correlate to: the number of characters to read from the file; the number of bytes per character; whether characters have been stored with the least significant byte first (.true) or most significant byte first (.false); a string of characters which can terminate the string being read; and relevant to that if the string is terminated parsing in a string into terminatedby will return the character which terminated it.
For our purposes we will begin by using the following code:
input.getstring(100,1)This will get the first 100 characters of the input file, with a charsize of 1 (this is the norm for English as well as most western languages). You can of course change these and any variables in this tutorial to fit your purpose/preference, these are only guidelines and experimentation is always welcome.
However, on its own this code is not very useful, we need to set this equal to a string variable so we can return it and later on deal with it in more complex ways. The code, and then the output of the program thus far are:
sOutput = input.getstring(100,1)
end function sOutputThis is a very basic text document
It contains multiple lines
As well as numbers
135156.23
and s
In the example file, you are presented with several problems, most obviously the document is cut off: this could be solved by changing the number of characters we get from the document, but we will do something more useful. We are going to go through the file one line at a time, this means we will need a while loop.
while input.endofdata != .true
sOutput = input.getstring(100,1,terminator="{d}{a}")
end whileThis loop will give you the first 100 characters of the file unless it finds the newline character, in SIMPOL this is {d}{a}, this means that if you debug the program on each loop iteration it will give you one line from the file. The loop ends if input reaches the end of the data stream
At the moment if the program is executed only the last line of the file will be output. There are several ways in which we can deal with this. Often the whole line will not need to be output, but in our case, we want to see each line outputted to a file. We could do this with the LogHandler, which we have talked about here but in this case, we are going to output this using fsfileoutputstream
Output
Similar to the input we need to initialise and declare our output variable. There is only one difference between input and output initialisation, there is an extra variable in the output function that determines whether you overwrite the file or append to it.
output =@ fsfileoutputstream.new("output" + sOutputFile + "{d}{a}",iErrornoOutput)In our example, we are going to overwrite the previous data. We want to output each line to the file, this is done by putting the above code into the while. Additionally, this code adds the word “output” to the beginning of the line as well as a newline at the end.
Code
function main()fsfileinputstream input;fsfileoutputstream output;string sInputFile,string sOutputFile,sOutput;integer iErrorno;sInputFile = "inputText.txt";sOutputFile = "outputText.txt";iErrorno = 0;input =@ fsfileinputstream.new(sInputFile,iErrorno);output =@ fsfileoutputstream.new(sOutputFile,iErrorno);while input.endofdata != .truesOutput = input.getstring(100,1,terminator="{d}{a}")output.putstring("Output" + sOutput + "{d}{a}",1)end whileend function ""